Servicenow FSM Fundamentals & Implementation Course Knowledge Checks Q&A
FSM Fundamental Quick Guide PDF
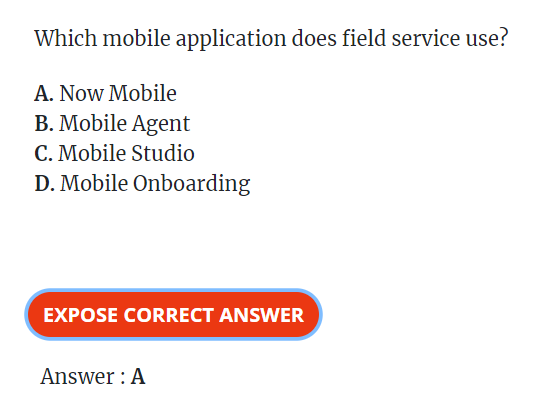
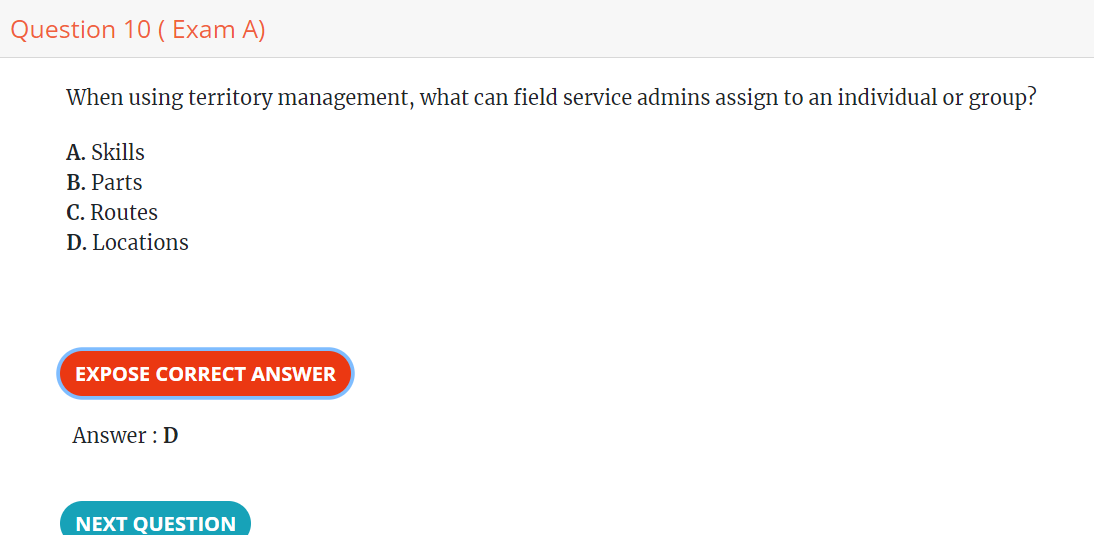
FSM Fundamental Overview 10 Questions
Work Order State 5 Questions
The Process Flow, found at the form's top, visually represents the current stage of the work order
request and task lifecycle. It advances when specific conditions are fulfilled.
Depending on an organization's business requirements, additional sub-states, such as ‘On Route’
and ‘Onsite Arrival’ can be activated and utilized

Work Order Initiation Process 5 Questions
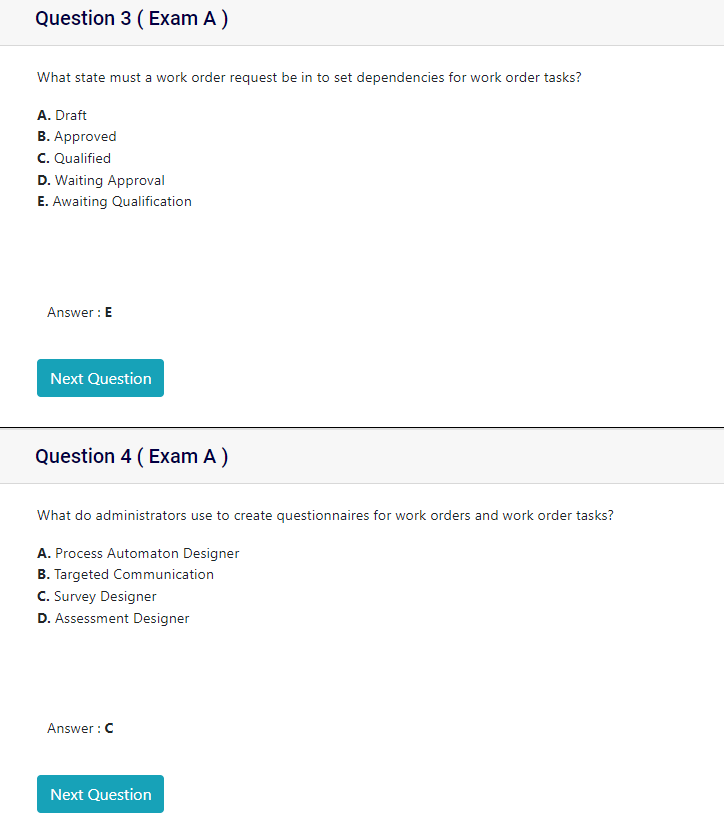
Qualification Process & Qualifier
- Reviewing and updating details of work orders and tasks.
- Optionally creating additional work order tasks.
- Defining task-specific requirements, such as parts and skills (optional).
- Establishing dependencies between work order tasks (optional).
- Assigning a dispatch group to each task.
- Officially qualifying each work order task.
Manual Qualification
Using Work Order Templates significantly streamlines the qualification process. Regardless of whether qualification is manual or automatic, tasks stemming from templates automatically shift to the 'Pending Dispatch' state if set to manual task assignment method (the default setting). This efficiency lets qualifiers concentrate on exceptional cases needing extra scrutiny and planning, optimizing their workload.
Upstream & Downstream Tasks
Work Order Qualification 6 Questions
Scheduling and Dispatching
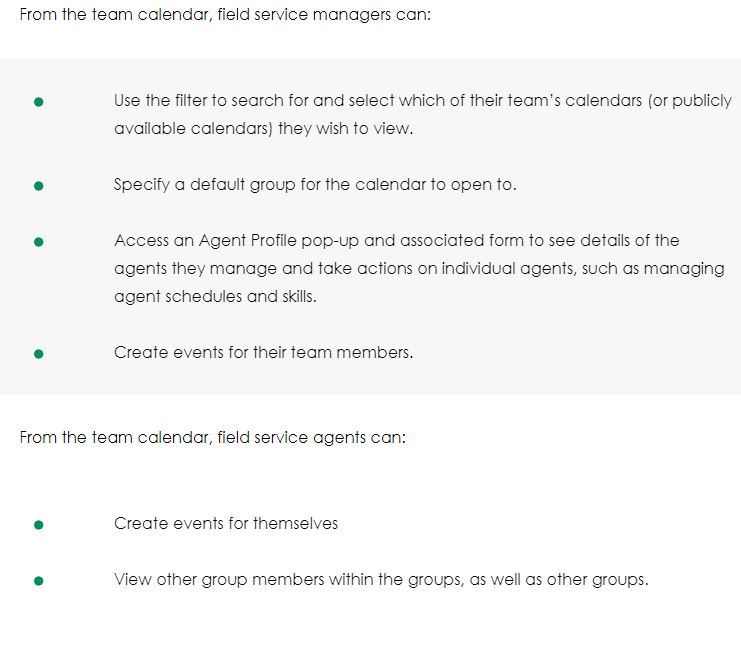
Persona
Field Service Manager
A Field Service Manager
manages team skills and schedules.
Field Service Dispatcher
A Field Service Dispatcher makes informed decisions about which tasks to assign to field agents.
Field Service Agent
A Field Service Agent manages their work schedule.
Geolocation
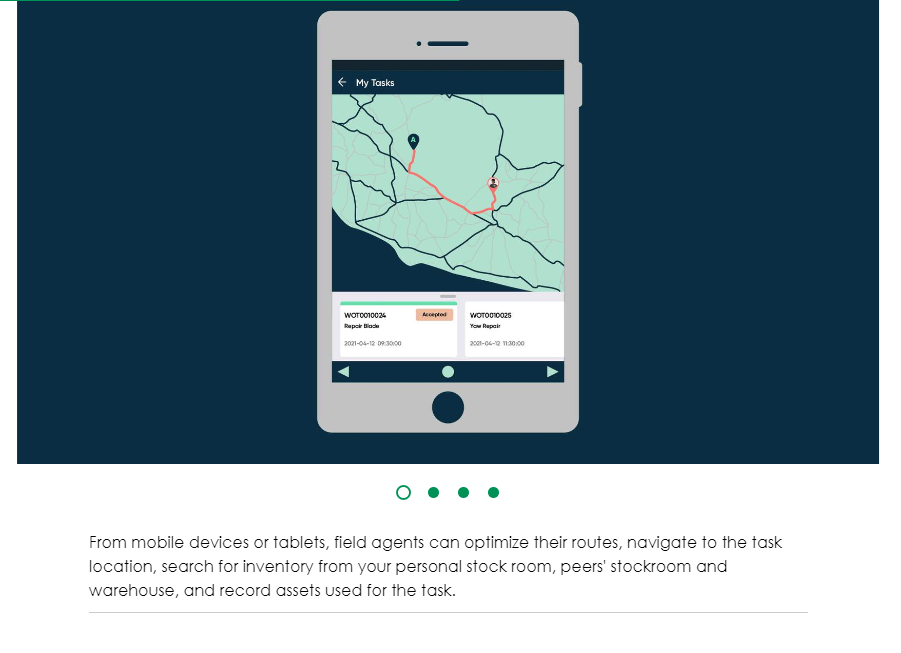
The Geolocation feature, utilizing Google Maps or alternative map integrations, enables user tracking, efficient route planning, and accurate travel time estimates to enhance the Field Service Management application.
Once activated and set up, geolocation facilitates task assignments by dispatchers to field agents, leveraging their real-time closeness to task locations, sourced from the latitude and longitude data from their devices or browsers. This continuous user location tracking refines business operations, especially in dispatching and fulfilling work order tasks. The system refreshes a field agent's location with every update they make to a task record, promoting frequent location updates. Moreover, dispatchers can ping devices to acquire agent geolocation at time-based intervals, such as every 10 minutes, ensuring up-to-date location data. Consequently, field agents and dispatchers can employ features like route optimization for streamlined scheduling.
For instance, consider a dispatcher at an internet service provider handling a work order concerning a router issue on Main Street. Using geolocation, the dispatcher can pinpoint the troubled router's exact location and view the positions of field agents in proximity. This visibility allows the dispatcher to allocate the task to the nearest agent, minimizing downtime.
Geolocation extends its utility to field service managers by offering real-time tracking of both agents and tasks. It not only facilitates immediate decision-making but also archives agent location histories. This valuable data can be harnessed for in-depth analysis, driving strategic initiatives to enhance service quality and operational efficiency
A system administrator initiates the geolocation configuration by installing the Geolocation plugin (com.snc.geolocation) and setting up the integration with Google Maps or another mapping service. To activate location tracking for field agents, the administrator simply needs to select the "Geolocation tracked" option in the User record. This comprehensive setup allows for precise location services, enhancing operational efficiency for dispatchers and field service managers.
Scheduling & Dispatching 2 Questions
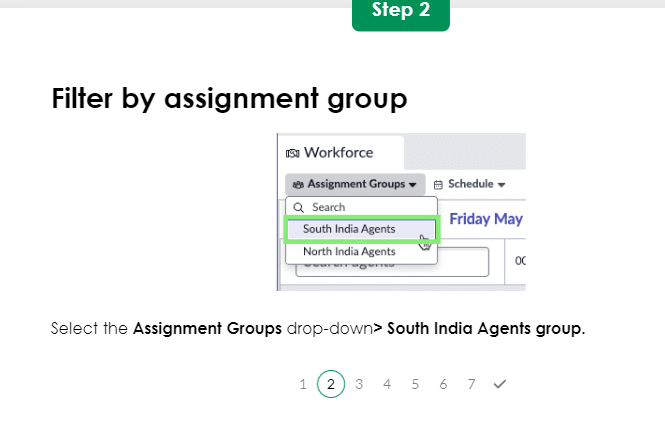
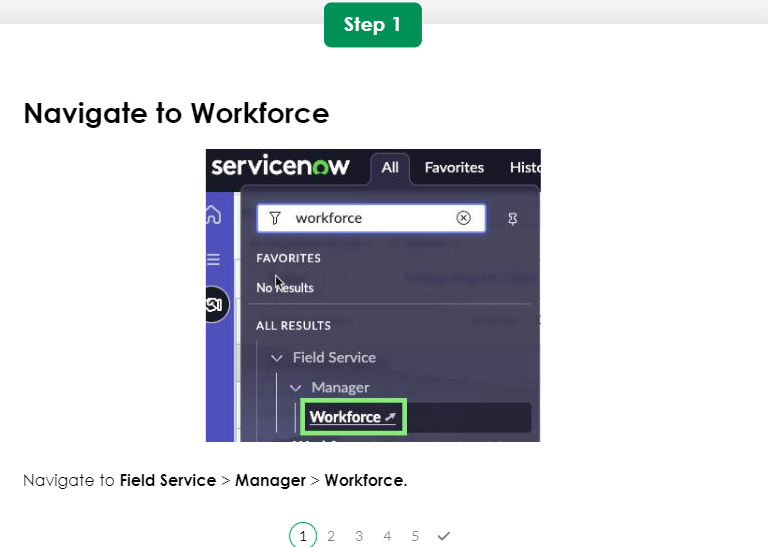
WorkForce Management
Manager Module
Delivery and Confirmation
Planned Maintenance for Field Services - 7 Questions
Implelementation Planning 12 Questions
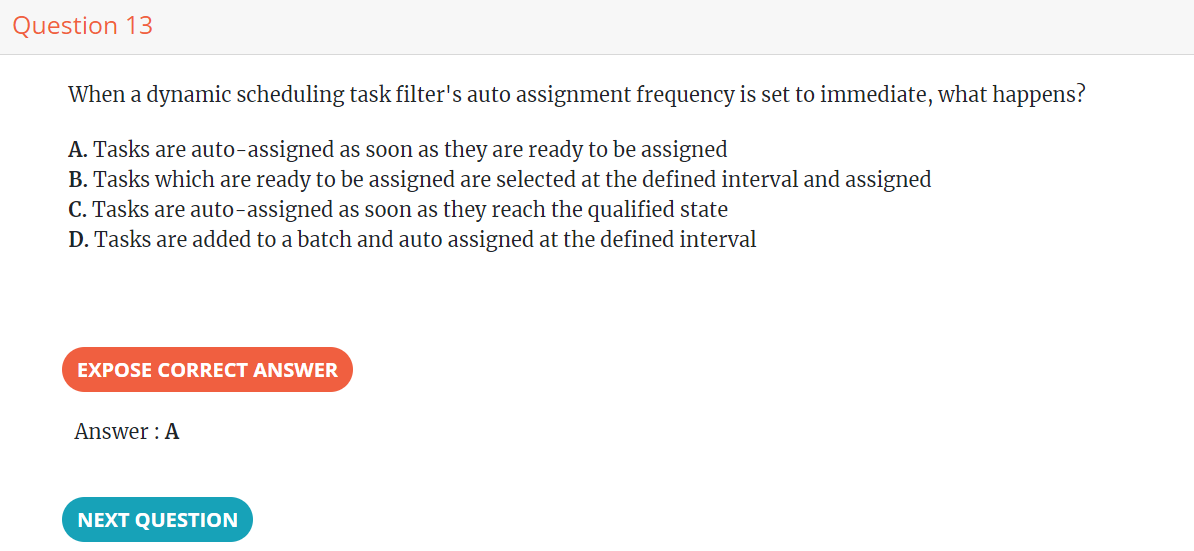
Optimization Scheduling and Dispatching Operations
Implementing Related Processes 28 questions
Answer - Advanced Map Pages
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/washingtondc-field-service-management/page/product/planning-and-policy/concept/c_DispatchWorkOrderTasks.html
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/utah-field-service-management/page/product/field-service-management/concept/using-dispatcher-workspace.html
Key Success Factor For Field Agent
The From Stockroom field is auto-populated with a default stockroom location, only if the part is available in the agent's personal stockroom or assignment group stockroom. You can specify a different stockroom location, if needed. Source : https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/vancouver-field-service-management/page/product/planning-and-policy/task/create-transfer-order.html
To automatically reserve the required parts in agent stockroom, enable the Reserve parts in agent stockroom configuration option on the Field Service Configuration screen.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/washingtondc-field-service-management/page/product/field-service-management/concept/using-rate-types-labor-rate-cards.html
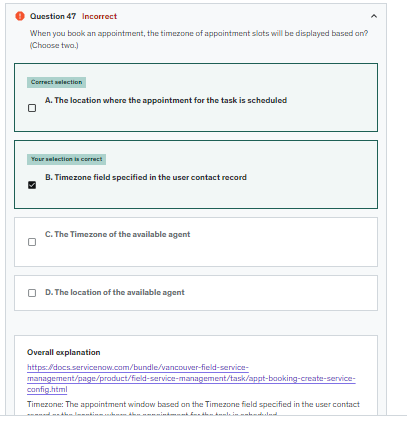
Timezone: The appointment window based on the Timezone field specified in the user contact record or the location where the appointment for the task is scheduled.
sn_fsm_disp_wrkspc.enable_optimize_route
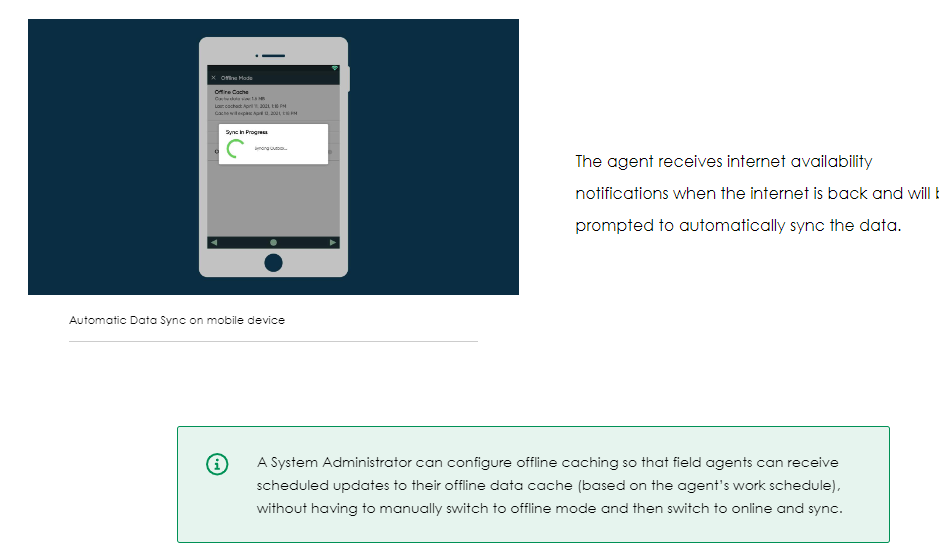
The duration when the cache expires on the client. Every time the payload is refreshed, this time gets extended.
After 48 hours, the system deletes the data due to a security protocol.
"create task filters to identify specific lists of tasks,"
The Optimize Task Routing scheduled job is inactive by default. When you set the active field for this scheduled job to true, the job runs every day at 3:00 am system time.
An organization may want to vary this by time zone or call it every hour (for work performed in busy cities). The scheduled job considers the tasks assigned to or accepted by agents on the current date and automatically optimizes the routes for those tasks.
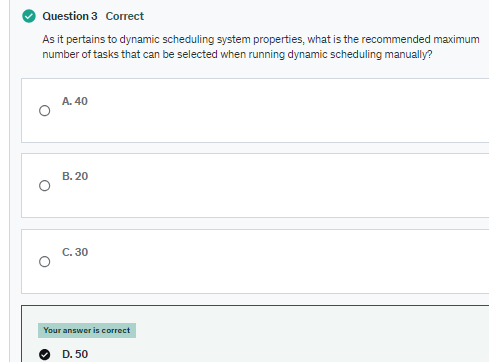
Note: To set the max number of tasks that can be selected when running dynamic scheduling manually, edit the com.snc.dynamic.scheduling.maxtasks system property It is recommended to not use more than 50 tasks at a time.
If you are ranking agents based on the number of parts available in the agent stockroom, you should configure the "Agents with most parts" matching criterion in the task filters.
Explanation: This criterion is specifically designed to identify agents who have the most required parts in their inventory. By using this criterion, dynamic scheduling can rank agents based on their stock availability, ensuring that tasks are assigned to those agents who have the necessary parts to complete them efficiently.

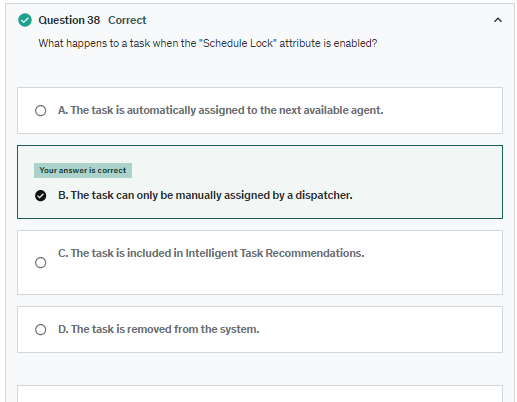
Tasks with Schedule Lock are excluded from Dynamic Scheduling and Intelligent Task Recommendations. Dispatchers still can manually assign these tasks.
Tasks are automatically locked under certain conditions such as:
Multi-Day Tasks
Needs Crew
Assigned/Accepted State
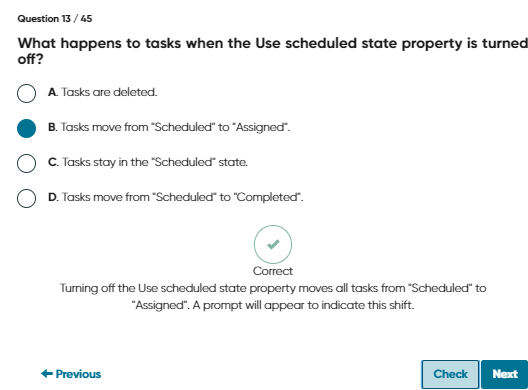
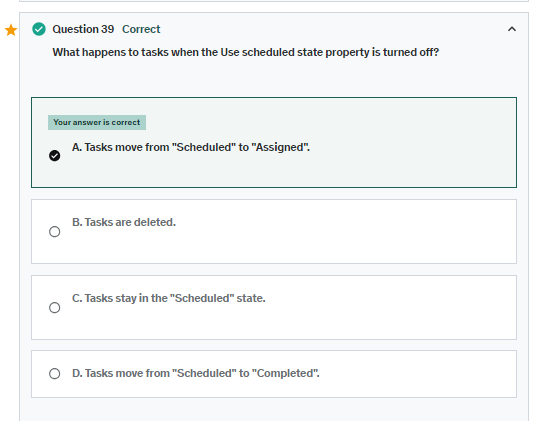
Note: If you turn the Use scheduled state property off, a warning appears indicating that tasks have moved from Scheduled to Assigned. Consequently, all work order tasks that are in the Scheduled state are moved to the Assigned state.
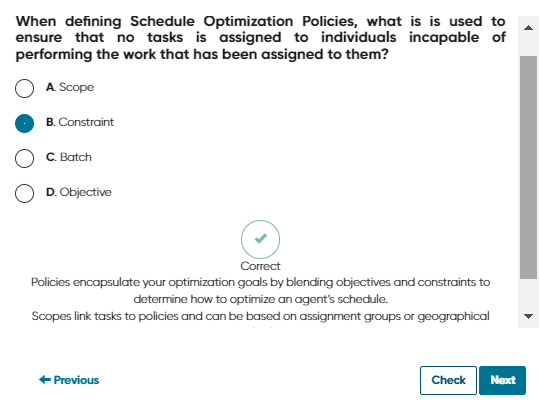
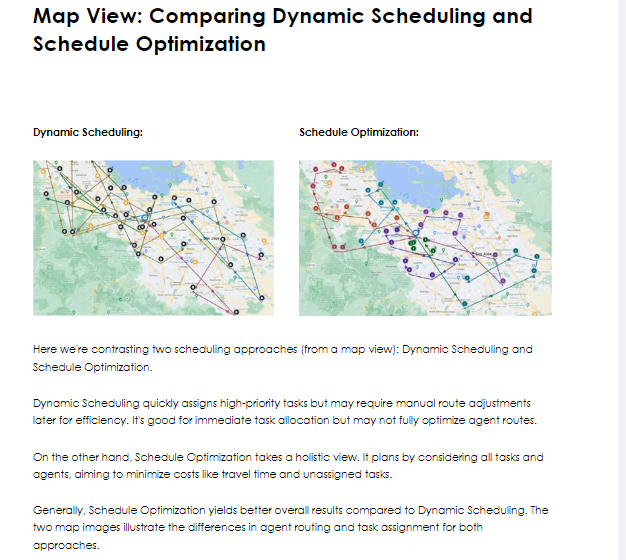
The main characteristic of Schedule Optimization in ServiceNow is that it uses a policy-based engine. This means it considers all assigned and pending tasks across all agents, analyzing multiple possibilities for task assignments based on defined policies and constraints to achieve global efficiency.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/washingtondc-field-service-management/page/product/field-service-management/task/create-an-optimization-batch.html
Agent will need role: sn_incident_read
Role is installed with the Incident Management for Field Service application
[wm_agent]
Manages actual task time and performs work on site. Agents can view parent incident details from the work order task.
Contains roles : sn_incident_read
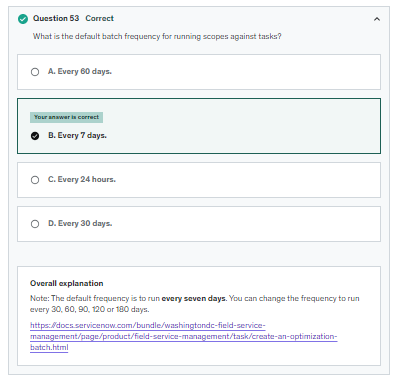
Note: The default frequency is to run every seven days. You can change the frequency to run every 30, 60, 90, 120 or 180 days.
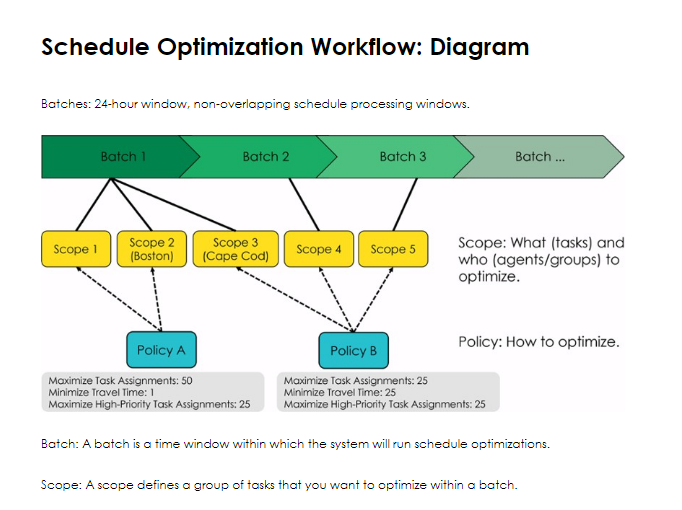
You can configure up to 36 batches within a 24-hour period for optimizations in ServiceNow Field Service Management. Each batch must last at least two hours, and there should be no more than three overlapping batches at any given time.
Field Service Capacity and Reservations Management enables Field Service managers to assign the appropriate amount of work to Field Service agents and contractor teams so that they are not overloaded with work beyond their defined capacity.
The capacity management process helps you plan work assignments based on priority and demand and ensure that business services are not unavailable due to being over capacity. Reservation rules within capacity management enable you to reserve a certain percentage of time for various tasks. Analyzing past failures and planning for the growth of demand for services help you manage capacity efficiently.
Overall explanation
Policies in Schedule Optimization combine objectives and constraints to reflect your optimization goals, enabling you to customize your optimization strategies effectively.
-------------------------------------
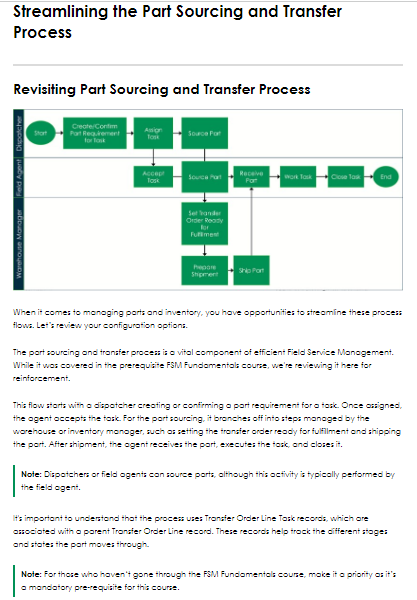
Agents must specify parts for the task, ensuring the correct parts are identified and reducing errors and delays.
Field Service Multi-Day Task Scheduling uses the value of the com.snc.wm.wo.task_window_days property to calculate the estimated end date of the task based on the schedule of a selected agent or crew.
The "Scheduling and Dispatch" phase is typically when tasks are assigned to field agents. This phase involves planning and allocating tasks, dispatching the field agents to the site, and ensuring they have the necessary resources and information to complete the work order.
Use Agent or Task Scheduling: This option allows for the automatic assignment of agents and the automatic selection of agents for tasks.
Auto-selection of Agents Considering Time Zone: This setting enables tasks to be assigned to agents based on the time zone of the agent, which can optimize scheduling and availability.
Priority Assignment: This feature allows priority-based assignment for automatically assigning agents. It requires that state flows be enabled, the process lifecycle must be task-driven, and auto-selection of agents based on agent or task schedules must be active.
Shift Scheduling for FSM: This setting allows for the consideration of agents’ schedules, skills, teams, and coaching to optimize the Field Service workforce. This is only available if Workforce Optimization for Field Service is activated.
Signature Capture and PDF Order Summary
Signature Capture Enable this option to include the name and electronic signature of the customer in the PDF work order summary.
PDF Order Summary Enable this option to create a PDF summary for a work order that includes completed tasks, parts used and returned, incidental expenses, and the time required to complete the work.
Use Document Template to generate PDF Summary Enable this option to create a PDF summary for a work order in a document template. PDF Order Summary
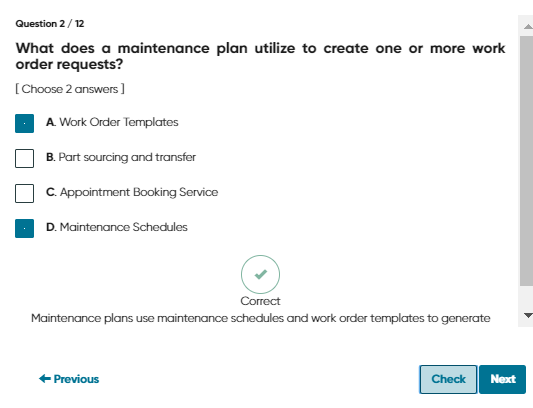
implementing a maintenance plan, particularly for HVAC systems:
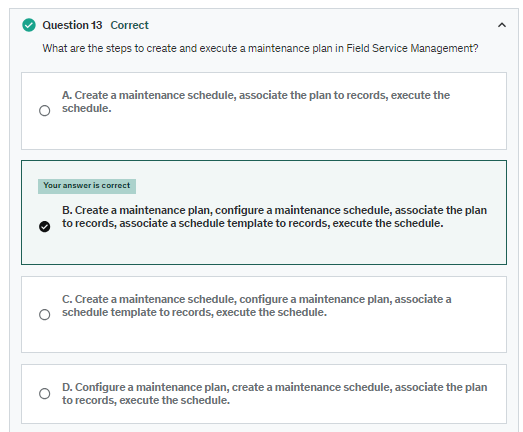
Develop a Maintenance Plan: Begin by establishing a maintenance plan, which defines what needs maintenance and the criteria for these tasks, such as the type of asset or its location. For instance, you could devise a plan to maintain all HVAC systems of a specific brand within a building.
Set Up a Maintenance Schedule: Decide on the timing of maintenance activities, including how frequently they should occur. For example, you might set up a semi-annual maintenance schedule for HVAC systems.
Link the Plan to Specific Records: Associate your maintenance plan with a filtered list of records that meet your defined criteria. For example, you could link the HVAC maintenance plan to all records of systems with a particular make and model in the building.
Attach a Schedule Template to the Records: Connect a schedule template that aligns with the timing defined in your maintenance plan to the appropriate records. An example would be attaching a semi-annual maintenance schedule to the selected HVAC records previously identified.
Execute the Maintenance Schedule: Implement the maintenance schedule either automatically according to the set timing or manually on demand based on immediate needs. For instance, in the event of a heatwave, you might conduct an unscheduled maintenance check on HVAC systems to ensure they are functioning optimally.
When field agents log their hours in 'time worked' records, corresponding time cards are automatically created or updated. This process is regulated by the time sheet policy. If necessary, administrators have the ability to stop this automatic creation for specific users by developing a specialized time sheet policy tailored to their needs.
Detailed Process Breakdown:
Record Time Worked: A field service agent begins the process by documenting the time spent on a specific task or non-task activity. This captures key data like the date, hours worked, and the category of work.
Generate Time Card: The system automatically generates a weekly time card from the recorded time. It consolidates all entries for that week into one category.
Create Time Sheet: From the time card, a detailed time sheet for the entire week is created. This document lists all activities and the hours spent on each for that week.
Manager Approval: After completion, the field agent submits the time sheet to their manager for review. The manager can approve or reject the time sheet based on its accuracy and completeness.
Convert to Expense Line: Following approval, the recorded time is converted into expense lines. This step is crucial for cost management as it transitions the time data into financial records.
Set of Tasks: Start by defining the tasks that need to be completed.
List of Agents: Filter down to agents who could potentially be assigned these tasks.
Task Time Windows: Identify the earliest and latest times tasks can start and finish.
Agent Schedules: Incorporate the standard working hours for each agent.
Agent Time-offs: Account for personal schedules, holidays, and requested time-offs.
Agent Tasks: Review the tasks already assigned to each agent.
Available Work Blocks: Based o
,
Batch
What: Optimizes tasks in batches for multiple field agents, considering all constraints.
When to Use: Beginning of the day or week.
Intra-day
What: Re-optimizes schedules for groups or territories in real-time based on changing conditions.
When to Use: When tasks are canceled, delayed, or new tasks come in.
To track agent location more accurately through mobile devices, the Geolocation plugin must be activated and configured. This plugin enables location tracking features necessary for monitoring agent positions and movements.
Schedule lock
Work order tasks that are marked for Multi day), Needs crew, or Assigned/Accepted state in sn_fsm.set_schedule_lock_by_state property are locked automatically for all scheduling mechanisms.
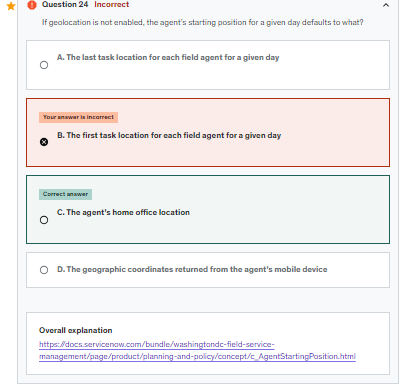
Agent starting position
If geolocation is not enabled, the starting position defaults to the agent's home office The Field Service Management application uses these criteria to locate work agents at the beginning of the day:
If the agent is routed for a future date, the system calculates the route from the home office.
If current geolocation data for the agent is available at the start of the day, the system uses those geographical coordinates instead of the home office as the starting point for the agent's routing.
If current geolocation data for the agent is not available for an agent at the start of the day or if geolocation tracking is disabled, the system uses the home office as the starting point.
If the agent has a task that is still Work in Progress at the start of the current day, the system starts the agent's route for that day at the location of the unfinished task. The start time is set to the time of the scheduled completion of the unfinished task or the current time, whichever is later.





























































































































































































































































































































































































Comments
Post a Comment